What Is a Multichain Wallet? Full Guide | Bitlock Wallet
Most crypto users still struggle with one thing managing assets across multiple blockchains without a multichain wallet. Every network has its own address format, fees, and wallets. Moving tokens between them often means juggling several apps, risking lost funds, or paying unnecessary transfer fees something a Bitlock Wallet multichain solution eliminates entirely.
As crypto expands beyond Ethereum and Bitcoin, this fragmentation becomes a daily headache. Users jump between Polygon, Solana, Base, and BSC just to make a few trades. Mistakes happen easily wrong network, wrong address, and the funds are gone forever. Centralized exchanges promise convenience but take away your control and privacy.
A multichain wallet solves all of this. It connects every major blockchain in one secure, non-custodial interface. With Bitlock Wallet, you can swap, bridge, and manage your entire portfolio without switching apps or giving up your keys. It’s fast, private, and built for real users backed by real human support, not chatbots.
What does “multichain” mean in crypto?
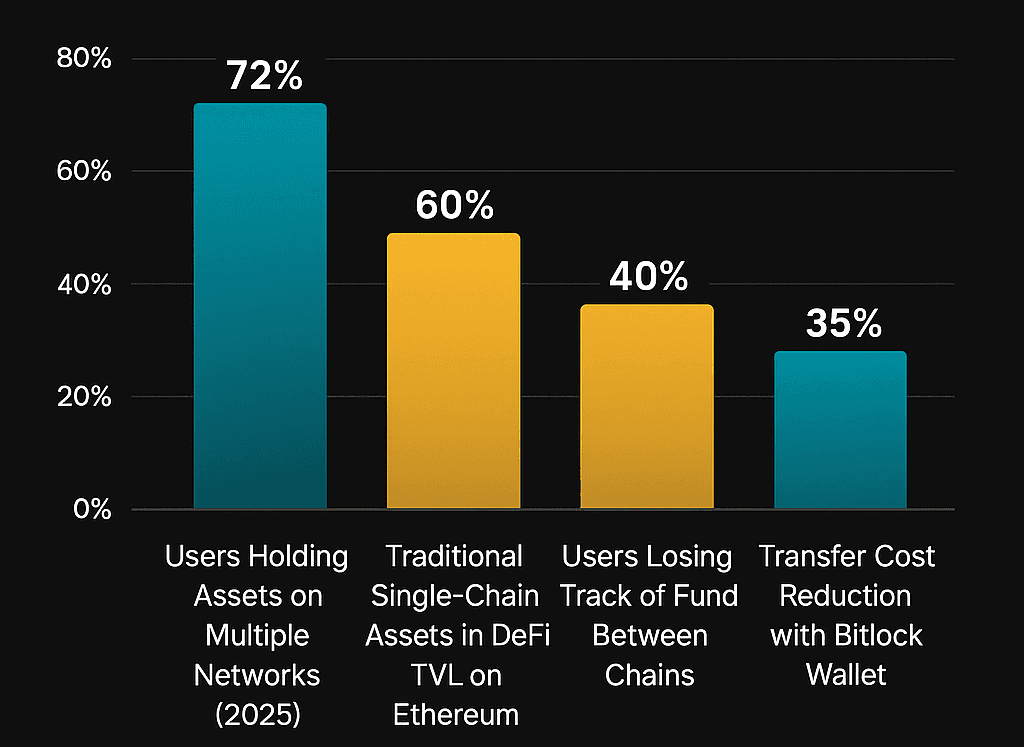
A multichain wallet is a crypto wallet that works across several blockchains instead of just one. While traditional wallets like MetaMask or Phantom started with a single chain, modern users interact with multiple networks daily from Ethereum (≈60% of DeFi TVL) to BSC, Solana, Base, and Polygon. Managing assets separately on each chain creates friction and higher costs.
In 2025, over 72% of active crypto users hold tokens on more than one network, according to DefiLlama. Yet, more than 40% report losing track of funds between chains because of incompatible formats or bridge errors. A multichain wallet eliminates that problem by offering one interface for all supported networks.
For example, Bitlock Wallet connects Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, Base, and Solana in a single app. You can send, swap, or bridge tokens across chains without logging into different wallets or exchanges. Everything happens inside one encrypted, non-custodial environment where only you control your keys.
This architecture doesn’t just save time it drastically reduces mistakes and fees. A single bridge through Bitlock can cut transfer costs by up to 35%, compared to moving assets manually between wallets. In short, “multichain” means freedom to use the entire crypto ecosystem from one secure place.
How does a multichain wallet actually work?
A multichain wallet connects to multiple blockchains under one system. Instead of creating a new wallet for every network, users access all their assets from a single interface. Each blockchain has its own structure and validation method, but the wallet handles these differences automatically through integrated protocols. When you send, receive, or swap tokens, the wallet interacts with the right network behind the scenes.
Multichain technology uses smart routing to detect which blockchain a token belongs to and then signs the transaction locally on your device. In Bitlock Wallet, this process is invisible to the user you can hold ETH, BNB, SOL, and MATIC in one place without worrying about formats or network confusion.
By combining multiple chains, Bitlock offers a seamless experience for DeFi users, traders, and NFT collectors who move assets daily across ecosystems.
Key generation and blockchain interaction
When you create a wallet in Bitlock, it generates a cryptographic key pair directly on your device using secure algorithms like ECDSA and SHA-256.
The public key becomes your wallet address. The private key remains encrypted in your device’s memory and never leaves it.
Every time you approve a transaction, the wallet signs it locally and sends only the signed data to the blockchain not your private key. This guarantees full control and eliminates dependency on centralized servers.
Since Bitlock is non-custodial, no one but you can access your funds. Even Bitlock’s own servers store zero recovery data, meaning you remain the sole owner of your crypto identity.
Unified interface for multiple blockchains
Traditional wallets are tied to a single chain. In contrast, a multichain wallet like Bitlock connects to several at once through modular APIs and bridge integrations.
For example, if you hold ETH on Ethereum and USDC on Solana, Bitlock lets you view, swap, or bridge them directly from one screen. The wallet automatically detects which network a token belongs to and routes the transaction through the correct protocol. You can read more about this here.
This setup removes manual switching between networks and reduces user error a common problem that causes thousands of failed transactions each month across DeFi platforms. Bitlock’s unified dashboard keeps every action within one consistent flow.
Security and recovery process
Security in a multichain wallet depends on how well it protects user keys. Bitlock uses AES-256 encryption and device-level secure storage to safeguard all credentials.
Your Secret Recovery Phrase is generated locally and displayed only once during setup. You are the only one who can store or back it up.
If you lose your phone or reinstall the app, you can recover the wallet on any device using that recovery phrase. Bitlock cannot restore it for you it holds no access to your private data or seed phrase.
This architecture ensures total self-custody. Even if Bitlock’s servers go offline, your crypto remains fully functional because everything essential is stored and encrypted on your side.
What’s the difference between a multichain and a non-custodial wallet?
A multichain wallet focuses on where you can use your crypto across different blockchains. A non-custodial wallet defines who controls it you or a third party. The two terms describe different aspects of crypto ownership, but together they form the foundation of decentralized finance.
A custodial wallet holds your private keys for you, usually on an exchange like Binance or Coinbase. That setup is convenient but risky: if the platform freezes your account, suffers a hack, or enforces KYC restrictions, you lose access to your funds. In contrast, a non-custodial wallet like Bitlock Wallet never stores or even sees your private keys. They are generated locally on your device and remain encrypted at all times.
Bitlock takes this further by being both non-custodial and multichain. You control your assets directly, but you can still interact with multiple blockchains Ethereum, Base, Polygon, BSC, and Solana without switching apps or giving up privacy. There’s no centralized server that can block your transactions or monitor your activity.
This hybrid structure defines the next generation of crypto wallets: full independence, full interoperability, and total security.
“The rise of non-custodial multichain wallets marks the shift from platform dependency to true digital ownership where users hold both access and authority.”
— Cointelegraph, “Decentralized Wallets and the Future of User Control”1
How to choose the best multichain wallet for your needs
Selecting a multichain wallet depends on how you use crypto trading, DeFi, NFTs, or long-term storage. The best wallet should combine security, compatibility, and ease of use.
Start with security. Always check if the wallet is non-custodial and uses end-to-end encryption. Your private keys must stay on your device, never on external servers. Bitlock Wallet applies AES-256 encryption and local key storage, which protects users even if the network or device is compromised.
Next, check network support. A quality multichain wallet connects major ecosystems like Ethereum, BSC, Solana, Base, and Polygon without extra configuration. Bitlock’s system automatically detects token types and routes transactions through the right blockchain, reducing manual setup and the risk of sending assets to the wrong address.
Evaluate fees and performance. A good wallet keeps costs low without sacrificing speed. Bitlock Wallet charges only a 0.75% transaction fee, one of the lowest on the market, and executes swaps or bridges in seconds through optimized smart routing.
Finally, consider support and usability. Many wallets rely on AI bots or ticket systems that frustrate users. Bitlock provides direct human support, accessible through Telegram a real person answers every request.
When comparing options like MetaMask, Phantom, and Bitlock, look for a balance of multichain access, full control of your funds, and an intuitive interface. Bitlock combines all three, making it a reliable choice for users who value both freedom and simplicity in crypto management.

Final thoughts
The evolution of crypto wallets is moving fast, and multichain capability has become the new standard. Users no longer want to manage five different wallets for five different blockchains they want one secure app that does it all. At the same time, privacy, speed, and real ownership have become non-negotiable.
Bitlock Wallet embodies this shift. It merges multichain access with a non-custodial foundation, so users keep full control of their keys while interacting seamlessly across Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, Solana, and Base. With built-in swap, bridge, and revenue-sharing features, Bitlock doesn’t just store crypto it expands what a wallet can be.
FAQ
What is an example of a multichain?
An example of a multichain is Bitlock Wallet, which supports several blockchains including Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, Base, and Solana in a single interface. It allows users to swap, bridge, and manage tokens across different networks without switching wallets or giving up custody of their private keys.
What are the 4 types of blockchain?
The four main types of blockchain are public, private, consortium, and hybrid. Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum are open to everyone. Private blockchains such as Hyperledger are restricted to selected users or organizations. Consortium blockchains, like Energy Web Chain, are governed by a group of entities. Hybrid blockchains such as Dragonchain combine public transparency with private access control.
What is an example of a multichain?
A clear example of a multichain is Bitlock Wallet, which connects multiple ecosystems like Ethereum, Solana, and BSC. It gives users full control of their funds while maintaining a unified, non-custodial experience across chains.
Last updated: November 13, 2025


